86-18144159516
86-18144159516
In today's interconnected world, the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a pivotal role in shaping the way we live and work. One crucial element that facilitates seamless communication and data processing in IoT ecosystems is the Edge Gateway. Let's dive into the intricacies of what an Edge Gateway is and how it transforms connectivity within the IoT landscape.
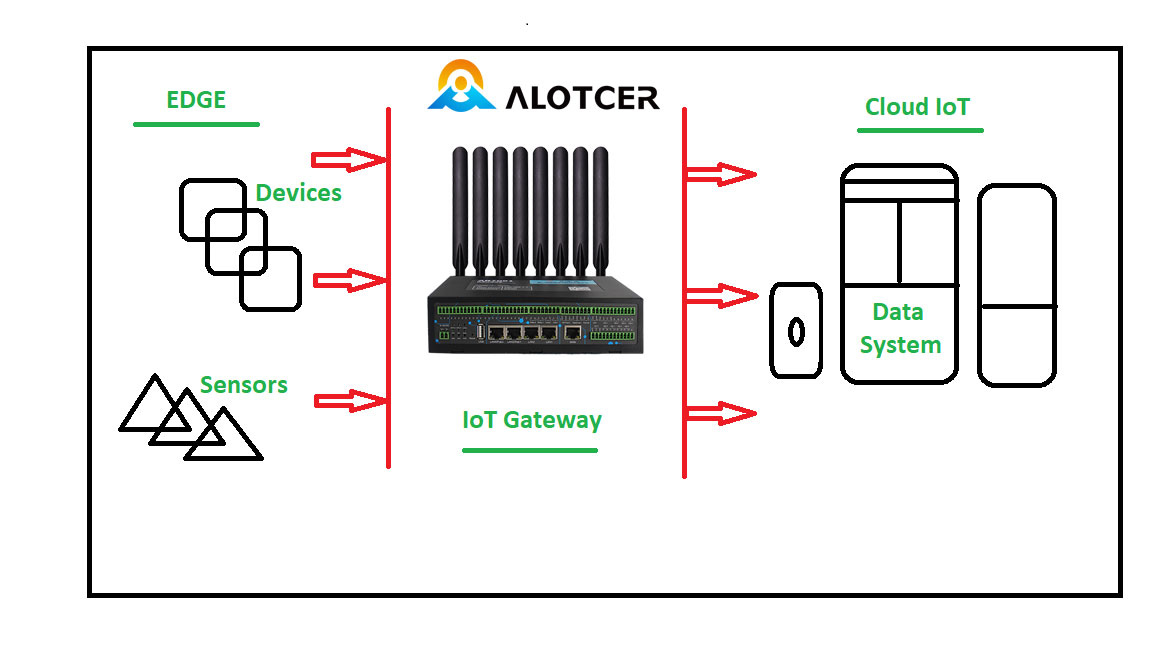
At its core, an Edge Gateway is a device that serves as a bridge between IoT devices and the central cloud infrastructure. It is strategically positioned at the edge of the network, allowing it to process data locally before sending it to the cloud. This localized processing capability distinguishes Edge Gateways from traditional gateways, making them a key enabler for efficient IoT operations.
The significance of Edge Gateways in IoT cannot be overstated. They play a pivotal role in enhancing the overall performance, security, and efficiency of IoT ecosystems. By processing data at the edge, these gateways reduce latency, optimize bandwidth usage, and enable real-time decision-making, making them a cornerstone of modern IoT deployments.
Edge Gateways interface with a myriad of sensors and devices within an IoT network. These can include temperature sensors, cameras, actuators, and various other IoT endpoints. The gateway acts as a centralized hub, collecting and managing data from these diverse sources.
To efficiently process data locally, Edge Gateways are equipped with powerful processing units. These units enable quick analysis and filtering of data before transmitting relevant information to the cloud. This local processing capability is crucial for applications that require real-time responses.
Edge Gateways boast versatile connectivity options, ensuring seamless communication with both IoT devices and the central cloud infrastructure. Wired and wireless connectivity options provide flexibility in deployment, making them adaptable to diverse IoT scenarios.
One of the primary functions of an Edge Gateway is to process and filter data at the edge of the network. This not only reduces the burden on the central cloud but also enables quicker responses to critical events, a crucial aspect in applications like smart manufacturing and autonomous vehicles.
Thanks to local processing capabilities, Edge Gateways facilitate real-time decision-making. In scenarios where split-second decisions matter, such as in healthcare monitoring or industrial automation, the ability to process data locally ensures timely responses without relying on distant cloud servers.
Edge Gateways play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of IoT ecosystems. By implementing security measures at the edge, potential threats can be identified and addressed locally, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring the integrity of the entire network.
The localized processing of data at the edge significantly reduces latency in IoT applications. This is particularly crucial in scenarios where real-time responses are imperative, such as in autonomous vehicles or remote healthcare monitoring.
Edge Gateways optimize bandwidth usage by transmitting only relevant data to the central cloud. This not only reduces data transmission costs but also ensures that the cloud is not overwhelmed with unnecessary information, leading to more efficient network operation.
With local processing capabilities, Edge Gateways contribute to enhanced reliability in IoT deployments. In cases of network outages or connectivity issues, these gateways can continue to operate autonomously, ensuring uninterrupted functionality of critical applications.
While Edge Gateways enhance security, they also pose unique challenges. Ensuring the security of data processed at the edge is crucial. Implementing robust encryption protocols and regularly updating security measures are essential steps in mitigating these concerns.
As IoT ecosystems grow, scalability becomes a concern. Edge Gateways need to be scalable to accommodate the increasing number of devices and sensors. Cloud-based management systems and modular architecture can address scalability challenges effectively.
Addressing security and scalability challenges requires a proactive approach. Regular audits, firmware updates, and collaboration with cybersecurity experts are essential in creating a resilient IoT infrastructure.
In industrial settings, Edge Gateways facilitate real-time monitoring of machinery, predictive maintenance, and efficient data analysis. These gateways are instrumental in optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Edge Gateways play a vital role in the development of smart cities. They enable intelligent traffic management, waste management, and public safety initiatives by processing data locally and providing actionable insights in real-time.
In healthcare, Edge Gateways are revolutionizing patient monitoring and healthcare delivery. These gateways ensure the confidentiality of patient data, enable remote monitoring, and support timely decision-making by healthcare professionals.
The future of Edge Gateways in IoT involves seamless integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. This will enable more advanced data analysis at the edge, further enhancing the capabilities of IoT applications.
Ongoing innovations in edge computing technologies will lead to more advanced and compact Edge Gateways. These innovations will address current challenges and open new possibilities for edge processing in diverse IoT scenarios.
As awareness of the benefits of Edge Gateways grows, their adoption across industries is expected to increase. From agriculture to retail, the transformative impact of these gateways will be felt across various sectors.
When selecting an Edge Gateway, ensuring compatibility with the diverse range of devices in an IoT network is crucial. Compatibility ensures seamless integration and optimal performance of the entire ecosystem.
Choose an Edge Gateway that can scale with the growing demands of your IoT deployment. A scalable gateway ensures that your infrastructure can evolve with the increasing number of connected devices and changing operational requirements.
Prioritize security features when selecting an Edge Gateway. Look for gateways with robust encryption, secure boot processes, and regular security updates to safeguard your IoT network from potential threats.
In conclusion, Edge Gateways play a pivotal role in shaping the efficiency and reliability of IoT ecosystems. Their ability to process data locally, reduce latency, and enhance security makes them indispensable in various industries.
As we look ahead, the integration of Edge Gateways with advanced technologies like AI and ongoing innovations in edge computing will further elevate their role in IoT. The future implications include more intelligent and responsive IoT applications that cater to the evolving needs of industries and consumers alike.
What is the primary function of an Edge Gateway in IoT?
How does an Edge Gateway contribute to reducing latency in IoT applications?
What are the key challenges associated with Edge Gateways in IoT deployments?
Can Edge Gateways operate autonomously in case of network outages?
How can organizations ensure the compatibility of an Edge Gateway with their IoT devices?









 Sitemaps
Other Country
Sitemaps
Other Country